The Complete Guide to Low-Code and No-Code Software Development
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
The software development market is radically changing. By 2026, the share of new applications built with low-code or no-code technologies will be 70 percent of applications (it was less than 25 percent in 2020). This radical change is not a fad itself, but a complete re-conceptualization of the process of software development, the people who are allowed to develop it, and how fast companies are able to develop it.
As a business leader who wants to speed up the digital transformation, a developer who wants to create a maximum amount of productivity, or an entrepreneur who wants to see his or her ideas being developed without needing to know a lot about the profound knowledge of various codes, this general guide will provide you with all the things that are necessary to know and use low-code and no-code development.
The low-code development platform market has reached $28.75 billion in 2025 with expectations that it will explode to reach to 264.40 billion in 2032 with a remarkable CAGR of 32.2%. The same trend is noticed in the no-code market, which will hit $102.7 billion by 2031. They aren’t only impressive numbers, but these are democratizing software development and it’s transforming whole industries.
What Are Low-Code and No-Code Platforms?
Low-code and no-code software development platforms are graphical software development tools that allow users to develop applications with little to no conventional programming. Rather than code thousands of lines of code, developers and business users operate under the intuitive drag and drop user interfaces, pre-built components and visual workflows.
Understanding No-Code Development
No-code systems are made by people with no programming background. These tools feature fully visual interfaces that allow users to create applications to the fullest functionality by configuring them using a point-and-click interface. Imagine it is a LEGO construction-block-building-up, all the parts have already been built and you just need to put them together to achieve whatever you want to have.
Key characteristics of no-code platforms:
- 100% visual interface with drag-and-drop functionality
- Pre-built templates for common use cases
- Limited customization but rapid deployment
- Ideal for simple to moderate complexity applications
Understanding Low-Code Development
Low-code platforms have little or no knowledge of code but can create custom code where necessary. They offer the flexibility to meet complicated requirements, yet they offer speed and efficiency of visual development. These platforms suit professional developers who wish to have quicker and simpler to use routines that do not compromise high complexity functionality.
Key characteristics of low-code platforms:
- Custom code can be written in a visual development.
- A higher level of flexibility and customization.
- Fits well in the complex enterprise applications.
- The professional developers and IT teams usually use it.
2. The Key Differences: Low-Code vs No-Code
Although both methods are intended to speed up the development, they are utilized by different users and purposes. The important thing is to know these variations in order to choose a platform that fits your needs.
| Criteria | No-Code | Low-Code |
| Target User | Business users, citizen developers, non-technical professionals | Professional developers, IT teams, technical users |
| Coding Required | Zero coding required | Minimal coding (10–20% custom code) |
| Complexity Level | Simple to moderate applications | Moderate to highly complex applications |
| Customization | Limited to platform capabilities | Extensive via custom code |
| Development Speed | Fastest (days to weeks) | Fast (weeks to months) |
| Learning Curve | Hours to days | Days to weeks |
| Best For | Forms, workflows, simple apps, MVPs, department tools | Enterprise apps, customer-facing apps, complex integrations |
3. The Business Case: Why Organizations Are Adopting LCNC

The fact that the rate of low-code and no-code adoption is so explosive is not incidental. Companies are more than ever under pressure to go digital with ongoing issues of developer shortages and application backlog. LCNC platforms are the solution to these issues.
The Developer Shortage Crisis
The demand of application is increasing five times as much as the IT capacity can provide. Conventional recruiting just cannot keep up, by 2024 80 percent of non-IT professionals will be working on the development of IT products and services, and more than 65 percent would be working with low-code or no-code development. This change is not merely a matter of bridging the gap, but it is a transformation of what software development can and should do to be dominated by.
Speed as a Competitive Advantage
A speed to market can or may break a business in the modern market. Compared to conventional means of development, low-code platforms can cut the development time by 90%. Projects that would otherwise take six months can be done in weeks. This speed is not only convenient to businesses that operate in fast moving markets, it is a survival requirement.
Cost Efficiency
Low-code platforms enable companies to reduce the development expenses by up to 70 percent. By not having to add two more developers, businesses can save an estimated 4.4 million after a period of three years. These are not fringe savings, but revolutionizing changes to development economics to render hitherto impractical projects economically viable.
Empowering Business Users
At the moment, 41 percent of the businesses already have active citizen development programs, and 20 percent are intending to implement them. The percentage of custom applications developed by non-IT employees has reached almost 60. This democratization of development implies that business users are able to self-service their problems without months of waiting until IT resources are available to them, and that organizational response times are significantly brought up.
4. Quantifying the Benefits: ROI and Performance Metrics
The articles about low-code and no-code development are promising, yet what is the actual data? We will look at the actual ROI measures organizations are getting.
Development Time Reduction
Organizations report drastic acceleration of development Speed:
- Reduction of development time up to 90% in comparison with traditional coding.
- Three months later, 72% of users are able to create and deploy complete applications.
- Without it, 56% of low-code-built solutions would not have been released within a reasonable time.
- Organizations develop software 56 times faster than the traditional methods.
Financial Returns
The ROI indicators are also quite strong:
- Average ROI of 253% within the first year
- No-code projects yield an average ROI of 2,560%
- 91.9% of projects recover their investment within the first year
- Full payback typically achieved in 6-7 months
- Up to 70% reduction in development costs
Resource Optimization
Beyond direct cost savings, low-code platforms optimize how organizations use their resources:
- Reduced by 70% in resources needed when compared to traditional platforms.
- Low-code is used in 80% of organizations to release developers to do more advanced projects.
- Less than five requests to apps are in backlog with 90 percent of low-code developers.
- Automation of claims processing reduced processing time by 80 percent.
Real-World Success Stories
Ricoh: ROI was 253% in seven months through the replacement of legacy systems with low-code solutions. The technology company has changed its application portfolio, cutting its maintenance costs by a very significant margin and increasing the rate of introducing new features.
Schneider Electric: Deployed 60 applications in 20 months. The multinational company used low-code to quickly modernize processes in several business units, and it realized ROI in seven months.
Georgia Tech: Saved $540,000 on programming costs. The school has used low-code systems in its operational efficiency and education, which significantly lowers IT costs.
5. Who’s Using Low-Code and No-Code? (Use Cases & Industries)
No-code and low-code platforms have been shown to be valuable in literally any industry and application. The following is the way various industries are taking advantage of these technologies:
Financial Services & Banking
Banks and financial institutions use low-code for:
- Onboarding and KYC of the customer.
- Loans processing and approval procedures.
- Reporting and regulatory compliance systems.
- Customer portals and mobile banking applications.
Healthcare
Low-code and no-code are used in healthcare organizations to find HIPAA-compliant solutions:
- Appointment and patient scheduling.
- Interpretations of electronic health records (EHR).
- Patient portals and telehealth platforms.
- Management and data collection of clinical trials.
Manufacturing & Supply Chain
The low-code solutions applied by manufacturing companies include:
- Inventory management system and systems.
- Workflow quality control and inspection.
- Management and procurement of suppliers.
- Resource planning and production scheduling.
Insurance
The insurance firms realize high efficiencies with:
- Artificial intelligence processing of claims (80 percent time saving reported)
- Underwriting and policy management processes.
- Customer service portals
- Applications of risk assessment.
Common Use Cases Across Industries
Recent statistics provide that most popular applications are:
- Form building and data collection (58% of users)
- Workflow automation (49% of users)
- Data visualization and dashboards (33% of users)
- Customer-facing applications (43% of users)
- Mobile applications and progressive web apps
6. Top Low-Code and No-Code Platforms in 2026

There are dozens of platforms competing in the market, and each of them has its advantages. By 2026, four out of every six big businesses will hire at the least four low-code tools. The most popular platforms in various categories are as follows:
Enterprise Low-Code Platforms
Microsoft Power Platform: Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI. Its strong integration with Microsoft 365 and Azure makes it suitable to organizations that are Microsoft-based.
Best for: Large enterprises, organisations with extensive Microsoft investment.
OutSystems: Low-code development platform with high-performance and built to develop complex and mission-critical applications. Supplies complete full-stack development services with good governance.
Best for: Enterprise applications requiring high performance and scalability
Mendix: platform with a powerful collaboration feature and a broad range of integration. Supported by Siemens. Very good with multi-clouds.
Best for: Organizations requiring multi-cloud flexibility and strong DevOps integration
No-Code Platforms for Citizen Developers
Airtable: Spreadsheet-database hybrid that makes complex data management accessible to non-technical users. Powerful for team collaboration.
Best for: Teams that require flexible database solutions but are not technical users.
Bubble: Complete no-code web application development platform. Provides a wide variety of design and database control.
Best for: Startups and entrepreneurs who are code-free builders of SaaS.
Webflow: Design-based no-code web building tool. Produces clean code that is production-ready.
Best for: it is best suited to designers and agencies that develop individual websites.
Workflow Automation Platforms
Zapier: Automate application integration across thousands of apps.. Easy drag and drop system to make integrations.
Best for: Businesses automating tasks across multiple SaaS applications
Make (formerly Integromat): Powerful automation platform, Workflow creator. Better than Zapier in complex cases.
Best for: Power users needing sophisticated automation logic
7. Implementation Best Practices
The low-code and no-code adoption will not be successful without more than picking a platform. Companies should ensure that they put in place a good governance, training and support frameworks.
Establish Governance Framework
Create clear guidelines for:
- Who is able to develop what kind of applications
- Security and compliance requirements.
- Policy of accessing and integrating data.
- Quality control measures and tests.
Start with a Pilot Program
Begin with a focused initiative:
- Select a high-impact but low-risk use case
- Form a small team of enthusiastic early adopters
- Measure and document results
- Use lessons learned to inform broader rollout
Invest in Training
Although low-code and no-code systems are simpler to learn in comparison to traditional programming, training is essential. Offer user support to learn how to build visual development, data modeling, workflow design, and platform-specific best practices.
Build a Center of Excellence
Build a hub of centralization offering templates, reusable elements, technical advice, governance supervision and ongoing training. It keeps quality and uniformity in the developmental process among the citizens.
Monitor and Optimize
Track key metrics:
- Number of applications created
- Development time saved
- Cost savings achieved
- User adoption rates
- Application performance and usage
8. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
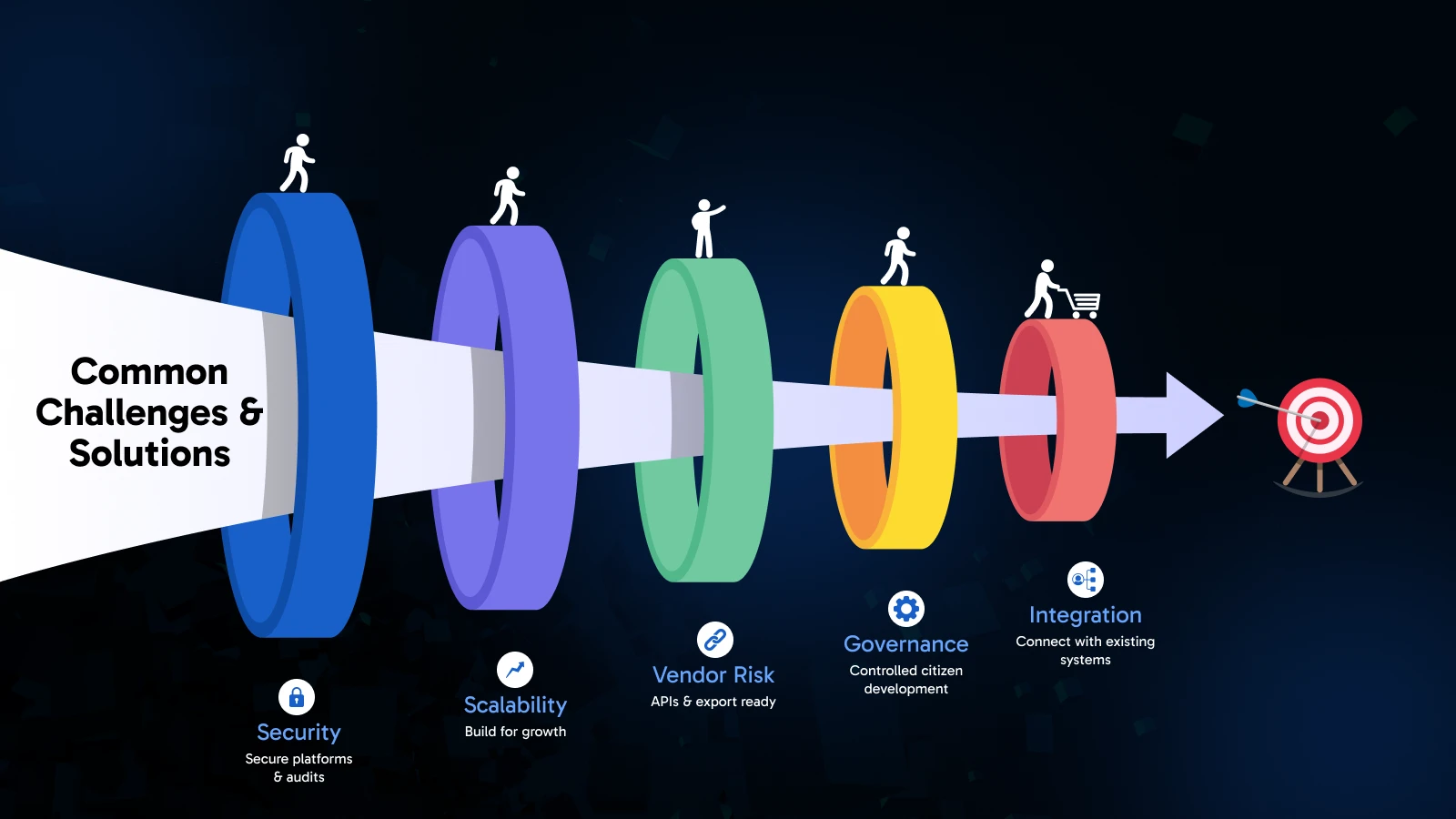
As the advantages are considerable, there are actual difficulties in implementing low-code and no-code platforms in organizations. It is important to know these barriers and ways of dealing with them to succeed.
Security Concerns
Challenge: 25% of organizations report security concerns with low-code platforms.
Solution: Select platforms with effective security capabilities, use appropriate authentication and authorization policies, perform frequent security audits, and deploy explicit data governance policies. Contemporary enterprise systems have in-built security measures and compliance.
Scalability Issues
Challenge: 47 % of organizations have concerns regarding inadequate scaling of low-code apps.
Solution: Select platforms with load performance in mind, design a growth-aware architecture, and apply a hybrid model where needed-low-code when quick development is needed, custom code when using performance-intensive elements.
Vendor Lock-In
Challenge: 37 % are concerned about vendor lock-in.
Solution: Select those platforms which allow exporting data, provide API access, create standard code where it is possible, and are well-integrated. Look into the record and position of the vendor in the market before committing.
Shadow IT Risk
Challenge: Without a proper governance, citizen developers can develop unmanaged applications.
Solution: Adapt to lightweight governance structures with approval workflows, create a Center of Excellence to support and monitor, deliver approved platforms that fulfill IT needs, and create explicit policies whilst being developmentally agile.
Integration Complexity
Challenge: There is a challenge involved in linking low-code applications with the existing systems.
Solution: Choose platforms that have large existing pre-built connectors, adopt integration platforms as a service (iPaaS) offerings, define API-first architecture standards, and document patterns of integration to use.
9. The Future: Trends Shaping LCNC Development
The development of low code and no-code is still moving fast. The future stage of this revolution will be determined by several major trends:
AI-Powered Development
Low-code abilities are being magnified with the integration of AI. Sixty-five percent of enterprises currently employ AI in business operations and the low code platforms are becoming more intelligent with automation. The use of generative AI allows the creation of apps using natural language, as a developer has the ability to tell the site what they want, using plain English, and have the application created before their eyes. Intelligent workflow optimization, automated testing, and AI-powered suggestions are becoming the norm.
Composable Architecture
Organizations are transitioning to the composable enterprise architecture where the applications are built as a combination of best-packaged business capabilities. Low-code platforms are ideal to this model where one can compose and recombine services quickly. In this way, it boosts agility and minimizes redundant development activities.
Industry-Specific Solutions
The market is seeing emergence of vertical-specific low-code platforms. Rather than general-purpose tools, these platforms come pre-configured with industry workflows, compliance features, and domain-specific components. In healthcare, financial services, and government sectors, there is an exceptionally elevated advance in this sphere.
Fusion Teams
The future does not involve displacing the developer, but it is a fusion team comprising of professional developer, business analyst and citizen developer. Professional developers create complex components and create frames whereas citizen developers use these building blocks to address particular business issues. This model is maximally fast and technical.
Expanded Use Cases
Low-code is no longer limited to web and mobile applications. Some of the areas that are experiencing growth are IoT applications, blockchain integration, augmented reality experiences, machine learning model deployment, and edge computing applications. The platforms are becoming full-stack development platforms.
10. Getting Started: Your Action Plan
Ready to begin your low-code or no-code journey? Here’s a practical roadmap to get started:
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
Before selecting a platform:
- Inventory your application backlog
- Identify quick wins and high-impact use cases
- Determine who will be building (IT, business users, or both)
- Understand your integration requirements
Step 2: Choose Your Platform
Evaluate platforms based on:
- Ease of use for your target users
- Technical capabilities and extensibility
- Integration with existing systems
- Security and compliance features
- Pricing model and total cost of ownership
- Vendor support and community resources
Step 3: Launch a Pilot
Start small to prove value:
- Select one department or use case
- Set clear success metrics
- Provide training and support
- Document lessons learned
- Celebrate and communicate wins
Step 4: Scale Thoughtfully
Build on your pilot success:
- Establish governance frameworks
- Create a Center of Excellence
- Develop training programs
- Build a library of reusable components
- Expand gradually to new teams and use cases
Conclusion: The Time to Act Is Now
Low-code and no-code development is not a new technology trend, nor is it a change in technology. It is a paradigm shift in the creation of software. As the market is forecasted to grow to 264 billion by 2032, and with 70% of new apps having adopted these technologies by 2025, the organizations who lag behind have a risk to be left behind by more agile organizations.
The statistics are self-explanatory: 90 percent of development time is reduced, ROI increases 253 percent, cost is saved by 70 percent, and the organizational agility is increased significantly. It has been proven that these advantages exist and can be realized by companies such as Ricoh, Schneider Electric, and many others.
Being a business leader who wants to gain competitive advantage, a developer who wants to achieve the highest level of productivity or an entrepreneur who needs to implement ideas in the quickest possible way, low-code and no-code are the proven ways to do it.
It is not about whether or not to use low-code and no-code development, it is about how fast can you start using it, and how successfully you can use these powerful platforms to change your organization.
Ready to Transform Your Development Process?
Our company is also dedicated to assisting organizations to deploy low-code and no-code solutions successfully. We can assist you whether you are new to the game or wish to streamline what you are already doing:
- Select the right platform for your needs
- Design and implement governance frameworks
- Build custom applications rapidly
- Train your teams for success
- Achieve measurable ROI quickly
Get a free consultation today, and find out how the low-code and no-code development will help us accelerate your digital transformation process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Low-Code and No-Code Development
1. What is the difference between low-code and no-code platforms?
Low-code platforms demand light coding and are aimed at professional developers who wish to create complex and scalable applications within a shorter period of time. No-code platforms use zero coding and are designed to be developed by business users or citizen developers to develop a simple application with visual interfaces. The main difference lies in technical flexibility, customization, and target users.
2. What are the main challenges of low-code and no-code development?
The most common challenges include:
- Security and compliance issues.
- Poor scalability of complex applications.
- Vendor lock-in risks
- Integration complexity with legacy systems
- Absence of governance that results to shadow IT.
These risks can be alleviated through appropriate platform choice, governance structures, and hybrid development frameworks.
3. Is low-code or no-code better for enterprise applications?
Enterprise applications are typically more suitable to be implemented with low-code platforms since they have custom code extensions, scalability, and sophisticated integrations. No-code platforms are best suited to in-house tools, workflows, and low-speed MVP creation but are constrained at enterprise levels.
4. What is cost optimization in low-code and no-code development?
Low-code and no-code development Cost optimization Low-code and no-code development Cost optimization Minimal manual coding that reduces the cost of software development and maintenance, rapid time-to-market, and reliance on extensive development teams. LCNC platforms have been reported to save up to 70% of costs and accelerate ROI by a significant margin.
5. Are low-code and no-code platforms secure?
Yes, the majority of low-code and no-code platforms of enterprise-grade include security measures (role-based access control, data encryption, audit logs, and compliance-certificates: ISO, SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR). Securing however lies entirely in the governance and platform setup.
6. Can low-code and no-code replace traditional software development?
Low-code and no-code are not substitutes of traditional development, but supplements. They should be employed to develop rapid applications and automation and traditional code is required to support high complexity, performance critical systems that are business-led.
7. Who should use no-code platforms?
No-code platforms would be suitable in:
- Business users and citizen developers.
- Marketing, human resource, finance and operations teams.
- Startups building MVPs quickly
- Teams needing internal tools without IT dependency
They give the non-technical users the ability to resolve problems on their own.
8. What industries benefit most from low-code and no-code?
Industries that have had the greatest adoption are:
- Financial services and banking
- Healthcare and life sciences
- Manufacturing and supply chain
- Insurance
- Education and government
These sectors have advantages of accelerated automation, workflows that are ready to comply, and fast digitalization.
9. What are the best low-code and no-code platforms in 2026?
Popular platforms include:
- Low-Code: Microsoft Power Platform, OutSystems, Mendix
- No-Code: Bubble, Airtable, Webflow
- Automation: Zapier, Make (Integromat)
The most suitable platform will vary based on your case, scale, security requirements, and intended users.
10. How do I choose between low-code and no-code?
To choose the right approach, evaluate:
- Application complexity
- Who will build the app (IT vs business users)
- Integration and scalability requirements
- Security and compliance needs
- Long-term maintenance and customization
A hybrid low-code + no-code approach allows maximum flexibility and is adopted in many organizations.