Understanding Zero Trust Architecture in Cyber Security
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
In the highly connected world today whereby employees work in their coffee shops, home networks and airports, the castle-and-moat style of security is no longer played. Hackers do not knock on the front door, they sneak in using a weak endpoint, stolen credentials, or unsecured cloud applications.
That is precisely what has made Zero Trust architecture in cyber security such a game-changer. Zero Trust does not presume that all of your network is secure but rather takes the opposite route: nobody and nothing is trusted by default, including users who are already within your networks.
What Exactly Is Zero Trust Architecture?
At its core, Zero Trust is built on a simple but powerful idea: “Never trust, always verify.” All users, devices, and applications should authenticate and have security posture before being allowed any access to any resource – and not only once, but on an ongoing basis during their entire time.
Therefore, a hacker can never move freely in the network even after penetrating past the login screen. Every step is checked. Every request is verified.
Why the Old Perimeter Model Isn’t Enough
Traditional security models relied on strong network perimeters — like digital walls around your data. But today:
- Teams are remote or hybrid
- Apps and data live in the cloud
- Threat actors are more sophisticated than ever
This has caused perimeter security to be ineffective. After the attackers have infiltrated, they will be able to walk freely. Cyber security Zero Trust architecture removes that blind trust and reduces the size of the attack surface to a sliver.
Real-World Impact
Take any recent data breach that made the headlines, there is a high probability that the attacker was able to gain access to the network through a single vulnerable point and then proceeded to spread out through it. Zero Trust makes such lateral movement almost impossible. They provide access on need-to-know and least-privilege basis and all activities are monitored, logged and verified.
No more discussion on constructing the walls of bigger size. It has to do with checking each door.
Core Zero Trust Architecture Principles

To have a picture of the functionality of the model of security, it is important to understand the principles of the Zero Trust Architecture. It is not a set of new tools but a change of mindset that transforms the way organizations perceive users, devices, and data.
Zero Trust does not establish a long-term broad access, but rather granular and contextual-based access, which responds to risk in real time. The three underlying principles that make it work are as follows:
1. Verify Explicitly — Trust No One by Default
All the users, devices and applications attempting to access your network should constantly be authenticated and approved.
It involves the multisignal approach of access decisions based on the user identity, device health, location, and behavior.
Even if someone has logged in, Zero Trust still keeps asking: “Are you who you say you are, and are you still secure?”
Think of it like an airport checkpoint that never stops verifying travelers at each gate.
2. Enforce Least Privilege Access — Give Just Enough, Just in Time
Least privilege principle is entirely about ensuring that minimum damage is caused in the event of account compromise.
Only the needed degree of access is provided to the users, and only as long as they require it. Administrative privileges do not last forever and confidential information is not accessible to just anyone.
This is a strong restriction on the distance of attackers within your systems.
When a hacker attacks a single account, he or she strikes the dead end rather than your entire network.
3. Assume Breach — Design as if You’ve Already Been Hacked
This is one of the pessimistic principles, but it is strong.
Zero Trust presupposes that attacks will occur as well – and creates mechanisms to limit and reduce the harm in the event they do.
These are micro-segmentation of networks, continuous monitoring, anomaly detection and auto response in real-time.
Zero Trust does not hope that everything will go well, but rather prepares in case all goes wrong.
Why These Principles Matter
All these Zero Trust Architecture principles combine to provide a proactive rather than a reactive security posture. They ensure that attackers do not hide within your systems and they are able to secure sensitive information even when your perimeter is breached.
Why Zero Trust Architecture Is Important
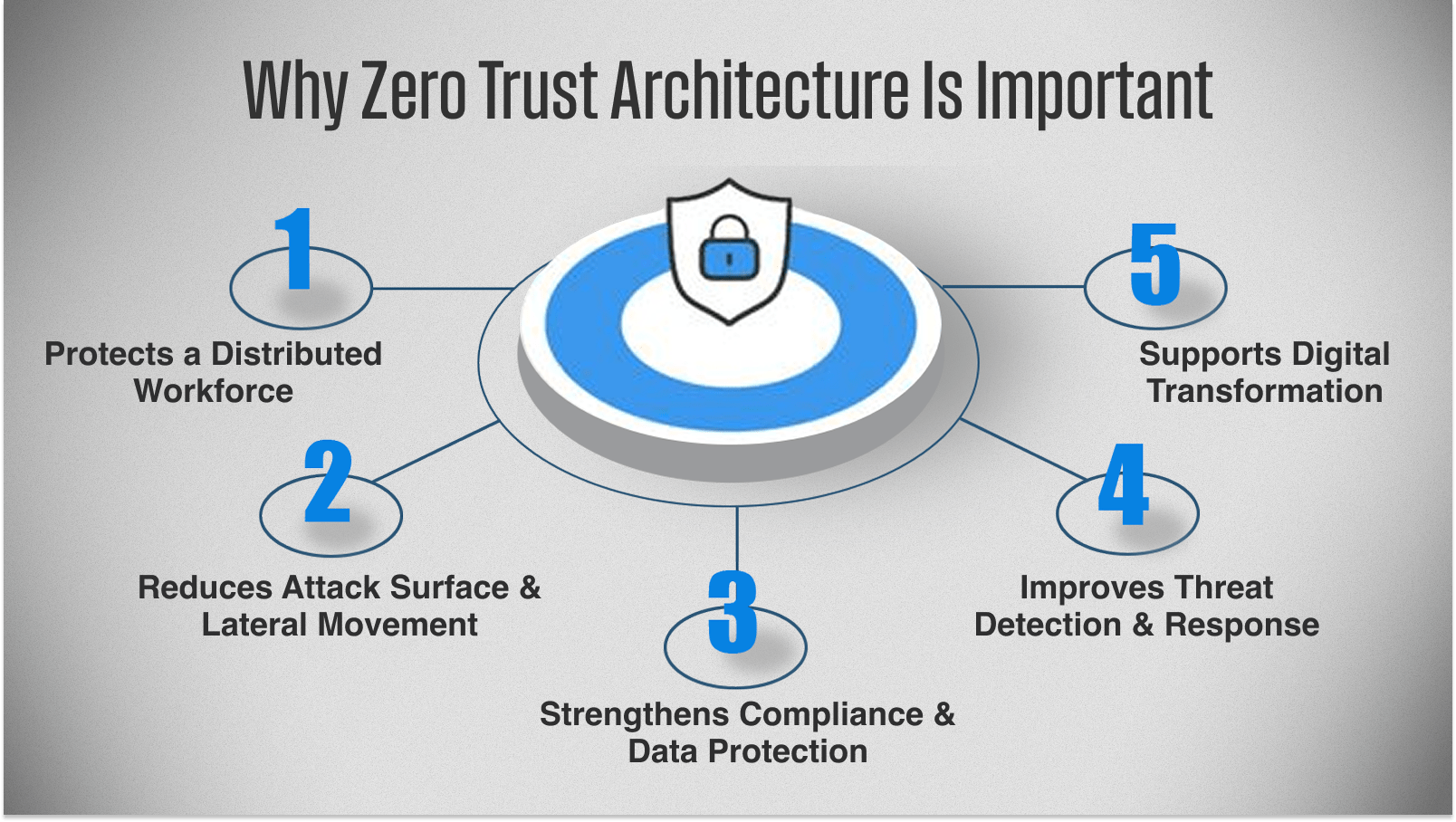
The question of why Zero Trust architecture is important is easy to answer: the old methods of securing information are no longer sufficient.
Businesses no longer have to be confined to office walls anymore, teams are becoming hybrid, data is being hosted in the cloud, and threats are omnipresent. In the absence of Zero Trust, all users and devices within your network are implicitly trusted – and that is what attackers are relying on.
This is why zero trust is no longer a choice:
1. Protects a Distributed Workforce
Zero Trust will have your team working either at HQ, a co-working space, or on top of their kitchen table, and they will be able to access the database securely regardless of their location of choice.
Instead of relying on a corporate VPN as a single gatekeeper, access decisions are made dynamically using identity, device health, and location data.
2. Reduces Attack Surface & Lateral Movement
Traditional networks give attackers a free playground once they’re inside. Zero Trust shrinks the attack surface and uses micro-segmentation to stop attackers from moving laterally across systems.
Even if one endpoint is compromised, the rest of your network stays safe.
3. Strengthens Compliance & Data Protection
Such regulations as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 mandate organizations to safeguard sensitive information and limit its access to the appropriate people.
Zero Trust implements minimal privilege access and comprehensive audit records – compliance can be demonstrated far more easily.
4. Improves Threat Detection & Response
Zero Trust is based on the concept of constant surveillance, which implies that the suspicious activity is discovered earlier.
Uncharacteristic activity e.g. when a user logs in on two different countries at the same time an alert or automated response is sent out.
5. Supports Digital Transformation
The use of clouds, SaaS and remote work are here to remain. Zero Trust offers the security base that businesses should rely on to scale confidently in such an environment without leaving loopholes that can be exploited by attackers.
In short, why Zero Trust architecture is important comes down to this: It keeps your organization agile, secure, and resilient against today’s evolving cyber threats.
AWS Zero Trust Architecture: Enforcing Zero Trust in the Cloud
AWS Zero Trust architecture now forms one of the foundations of successful digital transformation as businesses move to cloud environments at a rapid pace. In contrast to the conventional data centers, where security is based on a certain perimeter, cloud environments are dynamic, decentralized, and constantly changing, and that is why the principles of Zero Trust are necessary.
How AWS Implements Zero Trust
AWS doesn’t offer a single “Zero Trust product” — instead, it bakes Zero Trust principles into its entire cloud ecosystem. Its approach focuses on:
- Identity-Centric Security — All users, services and devices need to authenticate with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), with fine-grain access control to implement the least privilege access.
- Network Isolation and Micro-Segmentation — AWS restricts access across its resources by default with the help of Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), Security Groups, and Network ACLs.
- Continuous Monitoring — The services such as AWS CloudTrail and Amazon GuardDuty keep track of network traffic and user actions in real time and identify any anomaly in the network.
Benefits of Zero Trust on AWS
Applying Zero Trust architecture in AWS gives organizations:
- Stronger Protection Against Data Breaches — Any access request is authenticated minimizing the chances of unauthorized access.
- Scalability and Flexibility — Zero Trust policies are automatically scaled across accounts and regions as the cloud workloads increase.
- Improved Compliance Posture — Zero Trust controls are useful in addressing data protection laws such as GDPR, HIPAA and PCI DSS.
This makes AWS an ideal platform for enterprises adopting Zero Trust without sacrificing speed or agility.
Why AWS Zero Trust Matters
In the context of the multi-cloud and hybrid environments of modern organizations, AWS Zero Trust architecture will make sure that regardless of where the users and workloads reside, it is secure, context-aware, and constantly verifiable.
Why Zero Trust Architecture Is Important (and How to Implement It)
Organizations cannot afford to keep using the old approach of perimeter security in a cloud-first business world where remote workforces operate, and cyber threats are changing. This is the importance of Zero Trust architecture because it reinvents security in terms of identity and context, and constant verification, rather than location.
Adopting Zero Trust ensures every access request is verified, every session is monitored, and every resource is protected — no matter where it resides.
The Business Case for Zero Trust
Here’s why organizations worldwide are embracing Zero Trust as their core security strategy:
- Minimizes Breach Risk — Attackers are not allowed to move laterally even once they have managed to gain entry because of micro-segmentation and least privilege controls.
- Enables Secure Remote Work — Users can access data and apps everywhere without the use of the old VPNs, which are very insecure.
- Protects Cloud & Hybrid Infrastructure — Zero Trust secures applications, data and services on on-premise and cloud-based servers.
- Enhances Compliance & Audit Readiness — Good identity controls and their continuous logging are consistent with such regulations as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
- Reduces Insider Threats — The usage of strict access policy keeps users out of data that they do not require.
In short, Zero Trust aligns security with how modern businesses actually operate — distributed, dynamic, and digital.
Step-by-Step: How to Implement Zero Trust Architecture
Implementing Zero Trust isn’t about buying a single tool — it’s about shifting your security mindset and building a layered framework. Here’s a simple roadmap:
- Identify and Classify Assets You have to create a list of users, devices, applications, and data. Know their risk vulnerability and sensitivity.
- Verify Every User and Device Authenticate with multi-factors, device posture, identity governance and provide access.
- Map Access Workflows Understand who accesses what, when, and why. This assists in the development of least-privilege access policies.
- Define and Automate Security Policies Use context-aware policies (based on user, device, location, behavior) and automate enforcement with IAM, firewalls, and access gateways.
- Monitor, Test, and Continuously Improve Keep a close watch on the network traffic and user behavior so as to spot anomalies. Always review the policies and revise them as your environment changes.
Key Takeaway
Why Zero Trust architecture is important goes beyond security — it’s about building trust through verification. Organizations that adopt Zero Trust can move faster, innovate safely, and withstand modern cyberattacks.
Key Benefits of Zero Trust Architecture (and the Future Ahead)

Adopting Zero Trust Architecture is not only a defensive gesture but also a proactive strategy that places security in line with the reality of modern business. As organizations grow more digital, distributed, and cloud-driven, Zero Trust becomes the backbone of resilient cybersecurity. Here’s what makes it so impactful:
The Core Benefits of Zero Trust
- Stronger Protection Against Breaches All access requests are authenticated and the possibility of unauthorized access or horizontal movement is reduced.
- Enhanced Visibility & Control Centralized monitoring gives real-time insights into user behavior, device health, and network activity.
- Scalable & Cloud-Ready Meanwhile, it is designed to be compatible with both hybrid and multi-cloud setups with no slowness in its performance.
- Improved Compliance Posture The stringent access controls and audit logs of Zero Trust assist in fulfilling such regulations as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Resilience Against Insider Threats Least-privilege access controls are used to make sure that users can only access what they require and this minimizes internal attack spaces.
- Better Incident Response Restricting controls in granules will enable the rapid isolation of compromised accounts and devices and limit breaches.
Zero Trust: The Future of Cybersecurity
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, Zero Trust is shifting from an option to a necessity.
It offers organizations the nimbleness to enable remote people groups, assimilate new technologies, and operate at digital velocity and speed without influencing the security.
Zero Trust Architecture isn’t just about blocking threats. It’s about enabling business — safely.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re a startup or a large enterprise, now is the time to start your Zero Trust journey. Begin by evaluating your assets, applying least-privilege access, and building security into every layer of your infrastructure.
Because in today’s world, trust isn’t given — it’s earned, verified, and continuously enforced.
Frequently Asked Questions About Zero Trust Architecture
What is Zero Trust Architecture in simple terms?
Zero Trust Architecture is a cybersecurity model that is founded on the idea of never trust and always verify. In contrast to traditional security that trusts all that exists within a network, a Zero Trust constantly authenticates all its users, devices, and applications before they can access resources, whether they are within or without your network.
How is Zero Trust different from traditional security models?
Traditional security follows a castle-and-moat design and constructs high-perimeter walls but has faith in anything within. Zero Trust presupposes that no one can be trusted due to default; not even users who are already connected to your network. It is constantly checking identity, tracking behavior and restricting access depending on need, which ensures that even in case attackers penetrate primary defenses, they do not move around freely.
What are the three core principles of Zero Trust?
The three foundational principles are:
- Verify Explicitly – Verify any user, device and application on a continuous basis with a multitude of signals.
- Least Privilege Access – Aids access to minimum required access, but only as short as necessary.
- Assume Breach – Design your security as though attackers are already there and use segmentation and constant monitoring.
Is Zero Trust only for large enterprises?
No, Zero Trust is useful to both large and small organizations. But unlike big organizations, startups and small businesses can also enforce Zero Trust concepts in order to prevent the contemporary threats, particularly those based on cloud computing, remote employees, or accessible information.
Do I need to replace all my existing security tools to implement Zero Trust?
Not necessarily. Zero Trust is an approach and philosophy and not a single product. Most organizations begin with adding Zero Trust principles to their existing tools, whether by adding multi-factor authentication, least-privilege access, and better monitoring, before gradually extending their implementation of Zero Trust.
How does Zero Trust work with remote and hybrid teams?
Zero Trust is best suited to scattered workforces. Rather than just using location-based security decisions (such as being in the office) it uses identity, health of the device, and context to decide access. Your employees are able to work anywhere (at home, in coffee shops, and even in airports) without security issues.
What is AWS Zero Trust Architecture?
AWS Zero Trust Architecture implements the concept of Zero Trust in the Amazon Web Services. AWS achieves this by means of identity-based security (IAM), isolation of networks (VPC, Security Groups), and ongoing monitoring (CloudTrail, GuardDuty). It is intended to support companies with a cloud or hybrid infrastructure.
How long does it take to implement Zero Trust?
Implementation of a zero trust is a process and does not require a single project. Organizations usually begin with assets of high priorities and proceed to expand. A simple implementation can be finished in 3-6 months depending on the complexity of your infrastructure, whereas overall implementation may require 1-2 years. It all depends on taking things small and increasing.
Does Zero Trust slow down business operations?
When properly done, Zero Trust in fact allows businesses to operate faster and safer. The current Zero Trust systems rely on automation and context-based policies that allow authorized users to access the system with ease and prevent threats. The first one involves planning, yet the end outcome is more agile and secure operations.
How does Zero Trust help with compliance requirements?
Zero Trust is in a natural alignment with such regulations as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or SOC 2. With its essential characteristics such as least-privilege access, detailed audit logs, ongoing monitoring, and stringent access controls it responds directly to many compliance requirements, simplifying audits and minimizing the compliance risk.
What is micro-segmentation in Zero Trust?
Micro-segmentation separates your network into small areas that are isolated. Individual authentications and authorization are needed in each zone. This does not allow horizontal movement- when an attacker hacks one part they cannot automatically access the other parts. Having a variety of locked doors rather than a primary entrance is like this.
Can Zero Trust prevent all cyberattacks?
Although the Zero Trust is an effective risk mitigation tool with potential to minimize harm, no security model stays 100 percent safe. Nevertheless, the mentality of assuming breach with Zero Trust offers that despite attackers gaining access, they are isolated, tracked and cannot do much harm to the network. It also turns the potential disastrous violations into controllable incidences.
What’s the first step to start implementing Zero Trust?
Start by locating and categorizing your assets, users, devices, applications, and data. Know the most sensitive and those who should have access to what. Next deploy multi-factor authentication and begin implementing the least-privilege access policy on your most sensitive resources. Start at that and build up.
Is Zero Trust the same as Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)?
Zero Trust is the more general security model and philosophy, and ZTNA is a technological implementation of the principles of Zero Trust in accessing the network. ZTNA substitutes the old-fashioned VPNs with identity-based access controls. Consider ZTNA as a component of an even bigger Zero Trust toolkit.
How much does Zero Trust cost to implement?
The costs are diverse depending on the size of organization, the available infrastructure and solutions adopted. Zero Trust (such as access policies and MFA) features can be deployed at minimum cost with a few tools at hand. Cloud systems such as AWS have numerous Zero Trust features. Estimate money to use on tools, education, and even consulting support–but bear in mind the cost of a data breach is much more than Zero Trust spending.