Business Process Management (BPM): Transform Your Business Operations
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
In a modern business world where everything is based on speed, efficiency is not merely a bonus, but a must. Companies that have simplified their operations always outperform their competitors, offer superior customer experience and tend to adapt to the market changes in a faster manner. Business Process Management (BPM) comes in there.
You can be drowning in repetition, you can have bottlenecks in the processes or just want to scale your operation, BPM can provide a structured method to streamline the way work is done. This will be a complete guide, which will take you through all the essentials about BPM, basic concepts, and implementation strategies.
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Business Process Management (BPM) refers to a methodological approach used to find, model, analyze, measure, enhance and optimize business processes. BPM is a holistic approach to fully end-to-end business processes that produce business results unlike task management that applies to single activities and endeavors.
Consider BPM to be the orchestra director. All these instruments (or processes) can work separately, but when combined together with accuracy and timing they are even more powerful than the organization itself. At its core, BPM helps organizations:
- Trace the workflow of the business.
- Determine inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
- Equalize team and departmental processes.
- Basing continuously improved operations on data and metrics.
- Streamline operations to strategic business objectives.
BPM vs. Task Management vs. Project Management
BPM is easy to mix up with other similar notions, yet, it is essential to understand the differences:
Task Management focuses on the activities and to-do lists. It is concerned with accomplishing certain tasks but does not look at the bigger picture of the workflow.
Project Management is concerned with one off projects that have a start and finish date. Projects are short term undertakings whose deliverables are unique.
Business Process Management focuses on processes that are repetitive and ongoing that are the core of the business activity. The processes are endless and should be optimized.
To give an example, an onboarding of a new employee is a process that can be repeated (BPM), a quarterly budget report is a task (task management), and a new CRM system is a project (project management).
Why is Business Process Management Important?
The advantages of BPM implementation are much larger than mere efficiency increases. Companies that accept BPM experience radical changes on various fronts:
1. Increased Efficiency and Cost Savings
BPM gets rid of duplicates, bottle necks, and simplifies work flows. A smooth flow of processes ensures that work is done at a lower resource cost. This directly translates into cost savings- be it in terms of hours that labor is saved, errors are minimized or resources are distributed more efficiently.
2. Enhanced Customer Experience
When your internal processes are streamlined, customers get to sense it. More customer satisfaction is as a result of faster response time, uniform quality of service and reduction in errors. BPM makes sure that the customers do not need to repeat the same information or have an unequal service in one or another channel.
3. Improved Employee Satisfaction
Nobody likes a boring repetitive job. BPM eliminates repetitive work, and it establishes clear workflow so that employees can concentrate on high-value and meaningful work. Clarity in process ownership also minimizes confusion of roles and responsibilities which results into increased collaboration and job satisfaction.
4. Greater Agility and Scalability
Markets evolve, regulations and business needs change. BPM enables your organization to be more agile in that, it establishes flexible processes that may easily be changed. With a growing business, standardized processes can be scaled more readily, whether in new teams, new locations, or new product lines.
5. Better Compliance and Risk Management
Standard processes that are documented and standardized provide transparent audit trails. BPM not only ensures that all requirements are upheld by the regulations but also minimises the possibility of human error as well as giving the transparency of the who, what and when. This is especially important in highly controlling sector such as finance, health and manufacture.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making
BPM gives an insight of process performance in form of measures and analytics. You do not have to speculate on the problems locations, but have actual data on the bottlenecks, the cycle times and the resource utilization. This will be able to make intelligent choices on where to invest in improvement.
Types of Business Process Management
Business processes are not created equal, and there are various types of BPM that meet various requirements:
Integration-Centric BPM
It is the type that pays attention to processes that need little input of a human being yet highly need system integration. BPM based on integration integrates data between applications using APIs and automated data streams.
Common use cases: The automated exchange of customer data between the marketing automation and CRM systems, automated inventory management between supply chain systems, accounting software to accounting software.
Human-Centric BPM
Human-centric BPM is based on processes that involve human decision, approvals or knowledge. Such systems are usually characterized by easy interfaces whereby one can easily delegate duties, monitor the progress and even facilitate handoffs among the members of the team.
Common use cases: Workflow approval, hiring of employees, customer service ticket routing, approval and signing of contracts.
Document-Centric BPM
This kind is focused on documents which must pass through many phases of development, inspection, endorsement and implementation. Document centric BPM monitors document versions, signatures as well as making sure that the necessary approvals are secured.
Common use cases: Contracts, invoice, policy documentation, compliance reporting, mortgage application processing.
The Business Process Management Lifecycle
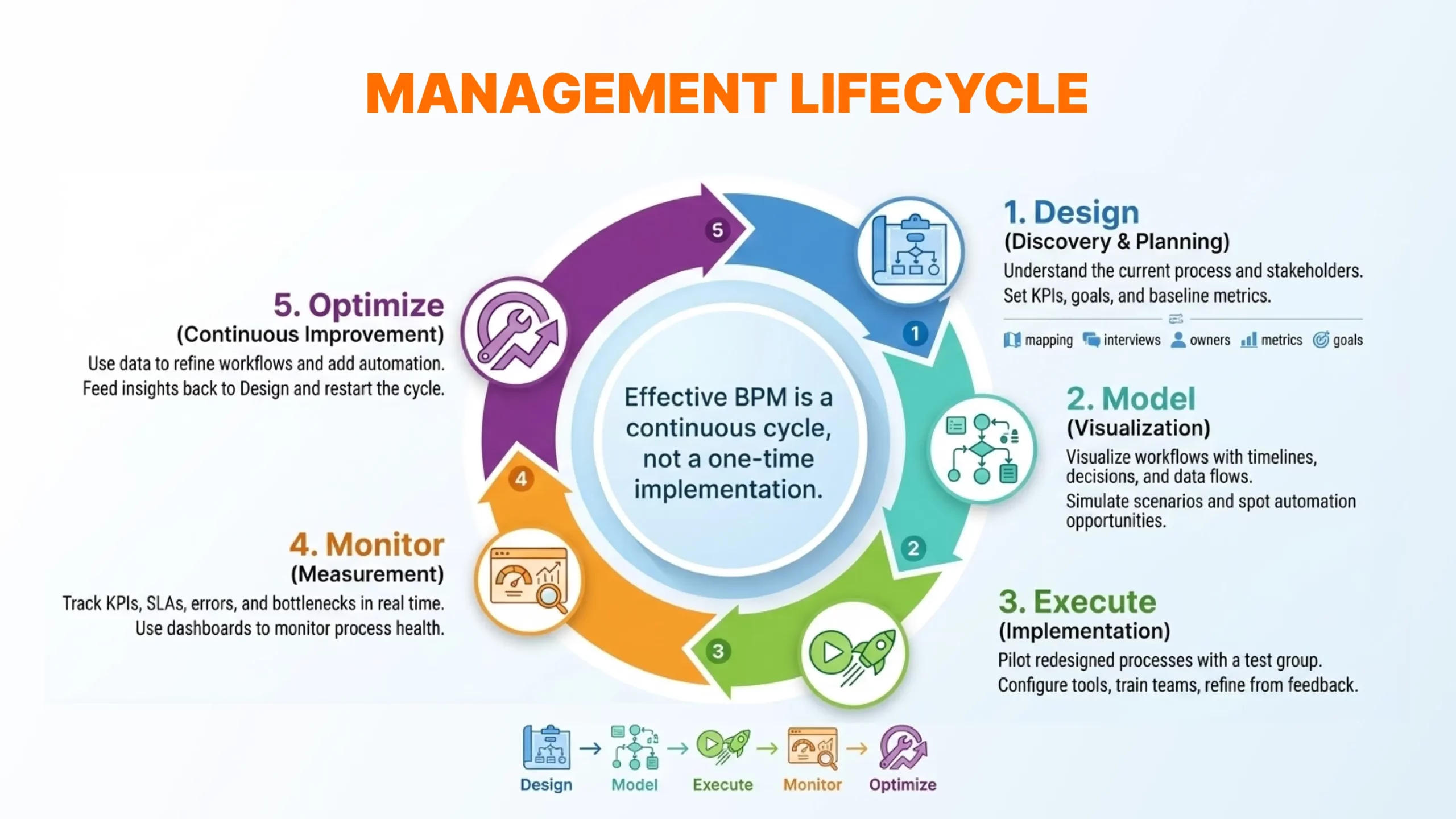
Effective BPM is not an implementation one time system but it is a cycle of improvement. BPM lifecycle comprises of 5 main stages:
1. Design (Discovery and Planning)
Begin by comprehending what you do now. Draw the flow for every step, find stakeholders and record the flow of work (not how it is supposed to flow). Set clear goals and KPIs on what success should be.
Key activities:
- Process mapping and documentation
- Stakeholder interviews
- Identifying process owners
- Setting baseline metrics
- Defining improvement goals
2. Model (Visualization)
Develop a visual depiction of your processes by way of flowcharts or process modeling software. Provide the detailed information such as timelines, decision points, data flows and system interactions. This form of visualization simplifies complex processes to comprehend and analyze.
Key activities:
- Creating process diagrams
- Documenting business rules
- Mapping system integrations
- Identifying automation opportunities
- Simulating process scenarios
3. Execute (Implementation)
Implement your process redesign with a pilot group before full implementation. This will enable the test of the new workflow, feedback and modification before going large-scale.
Key activities:
- Configuring BPM software
- Training team members
- Conducting pilot tests
- Gathering user feedback
- Refining based on real-world use
4. Monitor (Measurement)
Monitor performance of the processes with the KPIs that you were designing at the design stage. Keep a watch on the bottlenecks, delay, errors and other problems. Live dashboards and analytics will enable you to be aware of process health.
Key activities:
- Tracking cycle times
- Measuring error rates
- Monitoring SLA compliance
- Analyzing resource utilization
- Identifying new bottlenecks
5. Optimize (Continuous Improvement)
Apply the instruments of monitoring to effect improvements based on data. This could include the reorganization of workflows, resources, automation of more processes, or further work on the identification of bottlenecks found. Then the cycle begins again.
Key activities:
- Analyzing performance data
- Implementing process refinements
- Testing optimization changes
- Documenting improvements
- Restarting the cycle
Business Process Management Use Cases Across Industries
BPM brings value in virtually all industries and functions. The following are some of the strong practical applications:
Finance and Banking
Loan Processing:
BPM is a system used by banks to process the loan applications until they are approved and financed. The system manages document collection, credit checks, risk assessment and approvals and ensures that it remains in compliance with lending regulations.
KYC and Onboarding:
BPM simplifies the onboarding process of customers and automates identity verification, document collection, compliance, and account creation among several systems.
Healthcare
Patient Onboarding:
BPM manages the registration of patients, verification of insurance, gathering of medical history, and appointment scheduling and establishes flow of information between systems without violating HIPAA.
Claims Processing:
Insurance claims are processed using BPM, tracking their intake, validation, adjudication and payment, however exceptions are to be reviewed by humans.
Human Resources
Employee Onboarding:
Starting with the generation of the offer letter and the provision of equipment, as well as first day orientation, BPM gives the recruits a uniform, well orchestrated experience.
Performance Reviews:
BPM will automate the performance review process and create prompts, monitor completion, and reminders that the reviews are sent at the right time.
Customer Service
Ticket Resolution:
BPM directs customer inquiries to the appropriate department, monitors the status of these resolutions, and amplifies those that fall under the SLA levels.
Returns Processing:
BPM deals with the complete returns process, including authorization and inspection, refunding and updating the inventory.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Order Fulfillment:
BPM manages all aspects of the order capture, allocation, picking, packing, shipping, and delivery tracking and interfaces with various systems.
Supplier Onboarding:
BPM handles the registration of vendors, qualification, contract negotiation and system configuration which is consistent throughout procurement departments.
Content and Media
Content Publishing:
BPM coordinates the creation of content, its reviews, approval, localization, and distribution through many channels, as well as the rights and licensing management.
BPM Technology and Tools: What to Look For

The current BPM software is much more than a mere workflow management. The following are the key capabilities to be considered when examining BPM solutions:
Core BPM Features
- Visual Process Modeling: Drag-and-drop programming languages that allow business users to design workflows without programming.
- Workflow Automation: Automatic routing of tasks and notifications and inter-step handoffs.
- Business Rules Engine: Portable logic which controls the behavior of processes in various circumstances.
- Integration Capabilities: API and connectors to connect with the existing systems.
- Document Management: Version Control, Document storage and routing of process related documents.
- Analytics and Reporting: Dashboards and reports of process performance and bottlenecks.
Advanced Capabilities
- Intelligent Document Processing: Artificial Intelligence-based data mining of forms and documents.
- Process Mining: Automatic discovery of process behavior by analysing system logs.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Interaction with software robots which are capable of performing repetitive duties.
- Low-Code Development: Quick development of applications to meet unique processes.
- Mobile Access: Capability of accomplishing tasks and information on mobile devices.
- AI and Machine Learning: Routing intelligence, predictive analytics, and machine decision-making.
Best Practices for BPM Implementation
BPM implementation involves more than purchasing software in order to implement it successfully. Here are best practices that can ensure you have the highest probability of success:
Start Small and Scale
Do not try to change your whole organization simultaneously. Start small with one high impact process and then grow. This creates momentum and internal buy-in and enables you to learn and perfect your strategy.
Involve Process Owners Early
Indispensable insights are possessed by the people who live and breathe these processes on a daily basis. Engage them in process mapping, design and optimization. This also will create ownership and lessen the resistance to change.
Focus on User Experience
When your BPM system is not easy to use, workarounds will be discovered by people. Focus on user-friendly interfaces and processes that simplify the work of the users. Get a response and keep on improving user experience.
Measure What Matters
Establish meaningful and clear KPIs. Concentrate on measures that are related to business results such as levels of customer satisfaction, cost per transaction, cycle time, error rates, compared to the vanity measures that are not decision-making.
Embrace Continuous Improvement
Maturity in BPM is developed with time. Your initial version will not be perfect and that is alright. Form an environment in which the process improvement is constant, feedback is encouraged and optimization is inexhaustible.
Invest in Training and Change Management
New processes are necessary because new processes demand new behaviors. Offer extensive training, written documentation and continuous support. Explain the purpose of changes in order to make people see the returns.
Leverage Process Intelligence
Process mining and task mining tools can be used to gain insight into the current reality of how processes work. This disclosure of information shows concealed wastefulness and offers objective references of the enhancement.
Common BPM Implementation Challenges (and How to Overcome Them)
BPM implementations can be characterized as having foreseeable barriers irrespective of the best practices:
Resistance to Change
Challenge: Workers are accustomed to the old systems and do not trust new systems.
Solution: Engage users early, deliver clear benefits, offer superior training, and celebrate quick wins to generate enthusiasm.
Process Complexity
Challenge: Business processes are not as simple as they might have been thought, they have a great number of exceptions and edge cases.
Solution: begin by standardizing the happy path 80 percent of the cases. Exceptional cases should be processed by hand initially, but then progressively automatized, as patterns become evident.
Legacy System Integration
Challenge: Bridging an old system with the BPM software which does not have a modernized API.
Solution: Employ integration middleware or RPA to have a virtual connection between the legacy systems so that BPM can coordinate using the virtual connection.
Lack of Executive Support
Challenge: BPM projects fail due to lack of support in terms of leadership and resources.
Solution: Construct a powerful business case demonstrating ROI, connect BPM to strategic goals, and have an executive sponsor who promotes the initiative.
Over-Automation Too Soon
Challenge: Trying to automate all processes even without knowing what is really value adding.
Solution: Process optimization is the initial step, which is followed by automation. Automation of a bad process simply results in you failing sooner than otherwise doing something that should not be so.
BPM and Related Technologies: Understanding the Ecosystem
BPM doesn’t exist in isolation. Understanding how it relates to adjacent technologies helps you build a comprehensive automation strategy:
BPM vs. RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA uses software robots to automate particular repetitive procedures such as data input or processing a form. BPM coordinates the whole process and decides what tasks to be automated and organizes the work of people, system, and robots.
Think of it this way: RPA is the laborer who does the job. BPM, it is the manager who organizes work.
Together, they’re powerful: they can help participants determine where automation is appropriate and organize the entire process and RPA does the task execution.
BPM and Process Mining
Process mining acts on the logs of the systems to uncover how the processes are really carried out and shows the inefficiency and non-conformity to the workflow as intended. Better processes are designed by BPM based on these insights.
The relationship: Process mining delivers the information-based discovery that makes decisions about the BPM design and optimization.
BPM and Workflow Automation
Workflow automation aims at specifically directing work and information between individuals and systems. BPM also involves automation of workflow though it also involves process design, analysis, monitoring as well as optimization.
The relationship: Workflow automation is one of the aspects of the large discipline of BPM.
The Future of Business Process Management
BPM is developing at an alarming rate due to improvements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing:
Intelligent BPM
Machine learning and AIs are transforming BPM systems into smarter. You can anticipate greater predictive analytics anticipating the formation of bottlenecks, intelligent routing with the ability to learn the optimal course of action in each circumstance, and automated decision-making in common cases.
Hyperautomation
The combination of BPM, RPA, AI, process mining, and integration platforms can be used to automate more and more complex processes. Organizations are heading towards Lights-out processes which are autonomous and require people to be involved only to a limited scope.
Process Democratization
Both low-coded and no-coded BPM solutions are placing the design of processes in the hands of the businesses, rather than only the IT departments. This democratization helps to speed up the process improvement and enables organizations to be more flexible.
Cloud-Native BPM
The current BPM solutions are cloud-native, more scalable, can be deployed more quickly, and have the ability to integrate with other cloud products. This lowers overhead costs in infrastructure, and enables BPM to be accessed by any organization regardless of size.
Getting Started with BPM: Your Action Plan

Ready to begin your BPM journey? Here’s a practical roadmap:
Step 1: Identify a pain point. Select a frustrating process that is slowing down or making mistakes– a process where improvement will be seen.
Step 2: Map the current state. Record the way the process functions now, all steps, handoffs, systems, pain points, etc.
Step 3: Define success metrics. Create benchmarks and develop specific improvement objectives.
Step 4: Design the future state. Think outside the box and get rid of the waste and streamlining processes.
Step 5: Select appropriate tools. Evaluate BPM software that fits your needs, budget, and technical environment.
Step 6: Pilot and iterate. Test on a small scale, get responses, improve, and expand.
Step 7: Monitor and optimize. Monitor performance, discover new opportunities, and keep on improving.
Conclusion: Transform Your Business with BPM
Business Process Management is not about efficiency but about developing a company, agile, customer-oriented, and sustainable growth. This is by applying a logical method to the way work is done which carries out waste reduction, mistakes, enhance experiences, and liberate your people to concentrate in what is important.
This is because the organizations that will be successful in the modern competitive environment are those organizations that continuously optimize their operations. BPM offers the structures and the means to ensure that said optimization is systematic, measurable, and sustainable.
It doesn’t matter whether you are just starting to consider the process improvement or you are planning to move your already established BPM initiatives a step further, the thing is that you need to start. Select one process, and apply the principles suggested in the presented guide and feel the benefits on your own. When you develop momentum and you see success, increase your work. With time BPM becomes part of your organisational culture a constant dedication towards operational excellence.
The future is in organizations that work smart but not hard. You get there by Business Process Management.
Ready to optimize your business processes?
Start by assessing your current workflows and identifying the biggest opportunities for improvement. The journey to operational excellence begins with a single step—take it today.
BPM FAQs That Leaders Actually Ask Before Investing
1. BPM vs Workflow Automation: What Problem Does Each Really Solve?
Workflow automation is designed to move tasks from one step to the next. It works well for simple, predictable sequences like approvals or notifications.
Business Process Management operates at a system level. BPM designs, governs, executes, monitors, and continuously improves end-to-end processes that cut across teams, tools, and decisions.
A useful way to think about it
Workflow automation improves task movement
BPM improves how the business operates
If your organization only needs faster task routing, workflow automation may be enough. If you need visibility, accountability, compliance, and measurable improvement across departments, BPM is the correct foundation.
2. When Should a Business Choose BPM Over Basic Automation?
BPM becomes essential when processes
Span multiple teams or systems
Include decision points and exceptions
Require compliance tracking or auditability
Need ongoing optimization, not one-time automation
For example, automating an approval email is workflow automation. Managing procurement from request to payment across finance, vendors, and ERP systems requires BPM.
Organizations usually outgrow simple automation faster than expected. BPM prevents rebuilding workflows repeatedly as complexity increases.
3. How Quickly Can BPM Deliver Measurable Business Results?
Well-executed BPM initiatives typically show results within 8 to 12 weeks when approached correctly.
High-performing teams start with
One high-volume or high-pain process
Clear baseline metrics like cycle time or error rate
A focused pilot instead of enterprise-wide rollout
The fastest results come from fixing bottlenecks before automating them. BPM succeeds when optimization comes first and automation follows.
4. How Do You Build a Strong ROI Case for BPM?
Effective BPM ROI is based on measurable operational outcomes, not generic efficiency claims.
Key ROI drivers include
Time saved from manual handoffs and approvals
Reduction in rework, errors, and delays
Lower compliance and audit costs
Faster revenue realization from stalled processes
The most credible ROI comes from piloting one process, measuring improvement, and using real data to justify scale.
5. What Organizational Signals Indicate BPM Will Fail?
BPM struggles when
Processes are undocumented or disputed
No business owner is accountable for outcomes
Leadership expects software to fix broken processes
Change management is ignored
BPM is a discipline, not just a platform. Organizations that treat it as a governance and improvement practice consistently outperform those that treat it as a tooling exercise.
6. Why Do Most BPM Initiatives Fail While Others Scale Successfully?
Most failures follow three patterns
Trying to automate everything at once
Leaving ownership only with IT teams
Deploying systems that are harder than existing workarounds
Successful BPM programs
Start small and expand with proof
Assign business ownership with authority
Prioritize usability and adoption
Use data to guide continuous improvement
Technology enables BPM. Ownership and execution determine success.
7. How Does BPM Enable Enterprise Scale Without Operational Chaos?
BPM standardizes execution while preserving flexibility. It ensures processes behave consistently even as volume, teams, and locations grow.
With BPM, leaders gain
Real-time visibility into process health
Clear ownership and accountability
Controlled change without disruption
Confidence that scale will not introduce risk
This is why BPM often becomes the operational backbone for growing enterprises.
8. What Hidden Process Issues Does BPM Usually Reveal?
Once processes are measured, BPM commonly exposes
Unnecessary approvals
Unclear ownership
Manual work masked by email
Bottlenecks created by legacy dependencies
These issues rarely surface through observation alone. BPM makes inefficiencies visible, measurable, and correctable.
9. How Does BPM Improve Cross-Functional Collaboration?
BPM replaces informal coordination with structured accountability.
It creates
Clear handoffs between teams
Role-based ownership at every stage
System-driven visibility instead of status chasing
As a result, teams spend less time following up and more time executing.
10. How Does BPM Support Compliance Without Slowing Teams Down?
BPM embeds compliance into the process instead of enforcing it afterward.
It provides
Automatic audit trails
Rule-based approvals
Consistent execution across teams
Evidence for internal and external audits
This allows regulated organizations to move faster while staying compliant.
11. How Do Organizations Sustain BPM Improvements Long Term?
Sustainable BPM depends on continuous monitoring and iteration.
High-maturity BPM teams
Track performance metrics continuously
Refine workflows based on real data
Expand automation incrementally
Treat improvement as an ongoing cycle
BPM is not a one-time project. It becomes a continuous operating model.